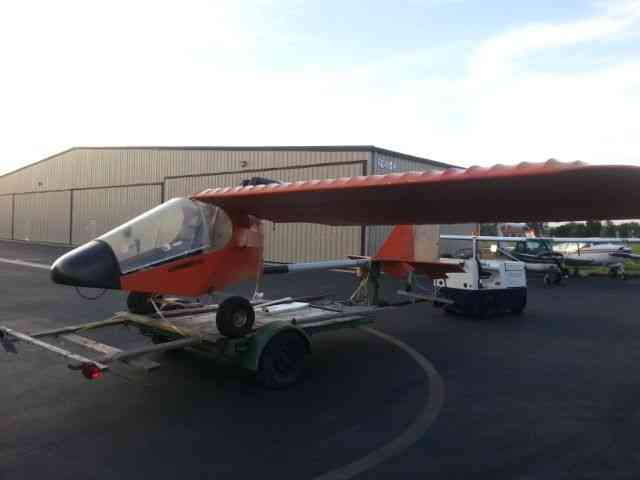
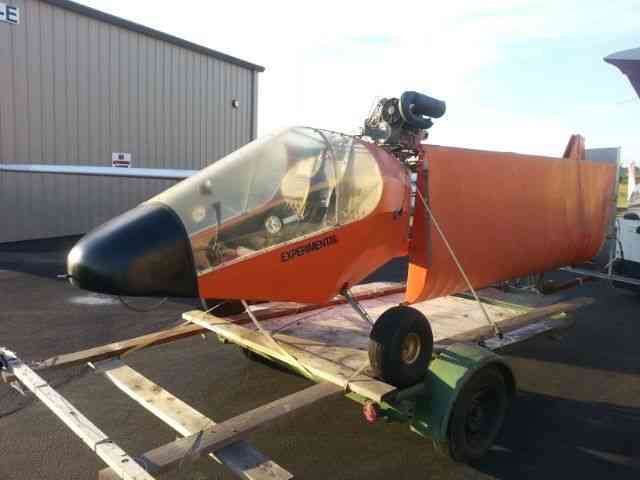
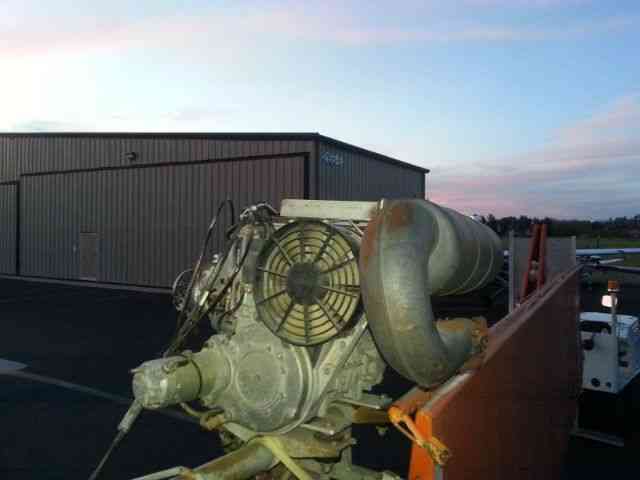
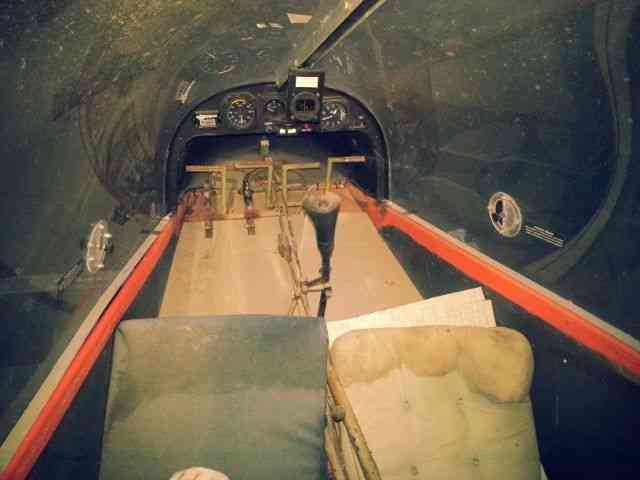
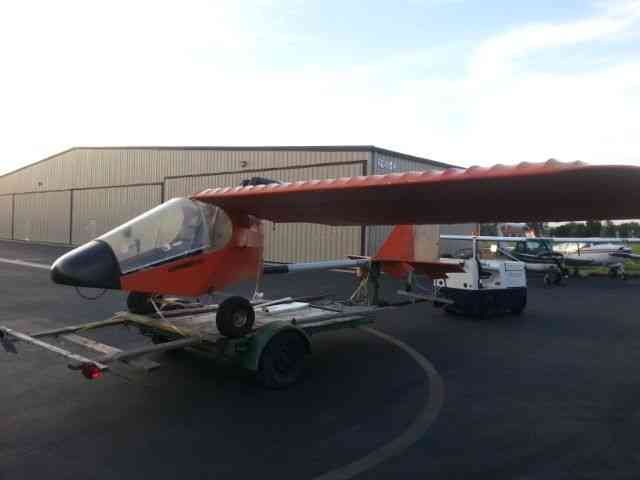
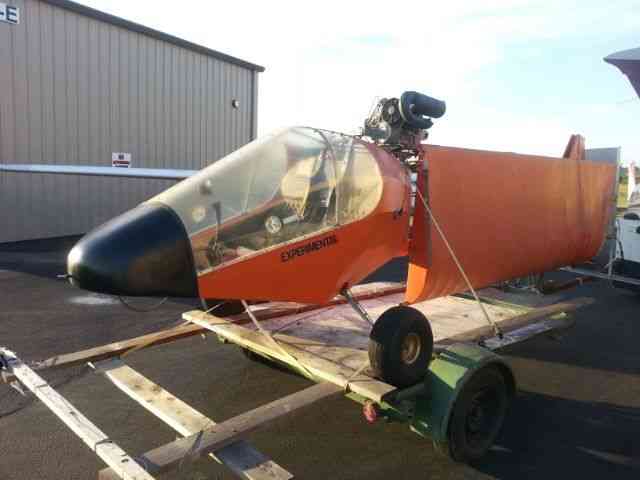
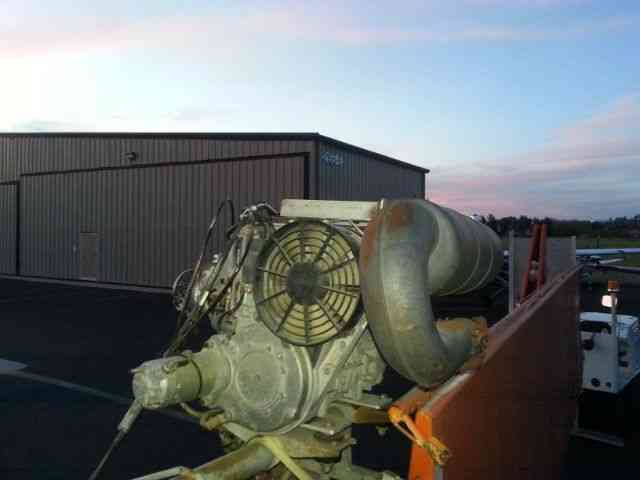
“Needs right wing assembly; L & R Wing support struts; connecting hardware and propeller. The rest.
Item specifics
| Used |
| “Needs right wing assembly; L & R Wing support struts; connecting hardware and propeller. The rest of the aircraft is complete.” |
| Make: | KOLB | Engine: | Bombardier Rotax 503 DCDI 50HP |
| Model: | Twinstar Mark II |
| *REASONABLE OFFERS ACCEPTED!!! Please feel free to contact seller with your interest and questions. Includes: Engine- Bombardier Rotax 503 DCDI with electric starter option. 2- 5 Gallon (10 Gal total) Fuel tanks with electric boost pumps. Extra options included: Pilot side heel brake pedals. 12V Electrical System Panel instruments: Airspeed indicator, Altimeter, Compass, Slip Indicator, Digital Tach/Hourmeter. AmeriKing 121.5/243 MHz ELT Sigtronics Transcom II Intercom Aircraft is on a heavy-duty custom trailer included with the sale. (Has current permanent CA trailer registration) Please contact seller with any questions about this aircraft. Sold: As-Is with no warranty to airworthiness or feasibility. Seller reserves the right to end sale at any time as item is for sale locally. $500 Deposit due within 24 hours of close. Balance due at pick-up. See payment details for full description and requirements. History of Kolb Aircraft: The first ultralight marketed by Kolb, the Kolb Flyer, was actually designed and built in the late 1960’s and flown in 1970. This was at least five years before John Moody made his first powered flights in his Easy Riser hang glider. The Kolb Flyer, after gathering dust for several years, was cleaned up and marketed as a kit in 1980 as Kolb’s first ultralight. It was one of the first ultralights that was actually a lightened and scaled down airplane, which happened to fit the FAA definition of an ultralight -- rather than starting with a hang glider and adding an engine. The Kolb Flyer was a 3-axis control, twin engine ultralight; it was powered first with 2 Chrysler West Bend engines, then later with 2 Solo engines.
The Kolb FireStar has been in production since 1985; it was an instant success and it still is! The major changes from the UltraStar were the placement of the engine on top of the wing allowing for a much larger diameter propeller; the addition of a nose fairing and short windshield (with provision for a full enclosure); and spring landing gear. In 1990, some minor styling changes were introduced resulting in the KX series. The rear cage on the original FireStar was covered completely right up to the wing; on the KX series the covering only goes about half way up -- the rest being left open for 360 degree visibility. The KX series may still be fully enclosed by the use of clear lexan windows around the rear cage, which still allows for 360 degree visibility. The cockpit sides were lowered on the KX series to make entry easier, and the windshield is full length up to the wing. The KXP was the KX with a stronger wing to accommodate the more powerful Rotax 503 engine: the KXP had 7 ribs (vs 5 ribs for the KX) per wing panel and a stronger drag strut arrangement. These additional items added only about 5-1/2 pounds to the FireStar KXP wings. The TwinStar series of two place airplane was introduced in 1984. First came the completely open TwinStar; later the TwinStar was enclosed and named the TwinStar Mark-II. Then in 1990, after the FAA allowed for heavier 2-place ultralights, the same basic design was strengthened (main spars increased from 5” to 6” dia.) to carry the more powerful Rotax 582 engine and also to increase the gross weight to 1000 lb. resulting in the TwinStar Mark-III. In 1993, the Mark-III lite was introduced. The lite version was discontinued in 1994 as most people wanted the flaps which the Lite version did not have. The Slingshot was introduced at Sun-N-Fun in the spring of 1996. The Slingshot was designed as a 2-place ultralight with a small wing and high cruise speed for the installed power, capable of delivering speeds comparable to a general aviation aircraft without the associated cost or complexity. In 1999, the company was purchased by a group of investors in London, Kentucky and became The New Kolb Aircraft Company. Under the management of this group, The New Kolb Aircraft Co. introduced the Mark III Xtra and Kolbra. In the spring of 2000, The New Kolb Aircraft Company introduced the Mark III Xtra by increaseing the width of the front end for aerodynamic reasons and moved the rudder pedals apart for better pilot comfort. Then moved the instrument panel closer to the pilot for easier access and better visibility. Upon introduction of the Mark III Xtra, the TwinStar Mark III was renamed the Mark III Classic. Later in 2000, the Kolbra was introduced. It is a fore-and-aft 2 seater, a larger version of the Slingshot. Upon development, two versions were introduced. Magazines referred to them as King Kolbra and its little brother. The difference in the two were higher cage size. The larger version won out and that is the version on the market today. Since its inception, more than 8,000 airplanes have been delivered world wide. |